Progressive cavity pumps are essential in various industries, known for their ability to handle viscous fluids and provide a steady flow. Understanding the components of these pumps is crucial for effective maintenance and operation. This guide delves into the key parts of progressive cavity pumps, their functions, and importance.
What is a Progressive Cavity Pump?
A progressive cavity pump consists of a helical rotor and a stator that work together to move fluids. The unique design allows for the efficient transfer of materials, including those with high viscosity, solids, and shear-sensitive fluids. The design also minimizes pulsation, making it ideal for applications requiring a consistent flow.
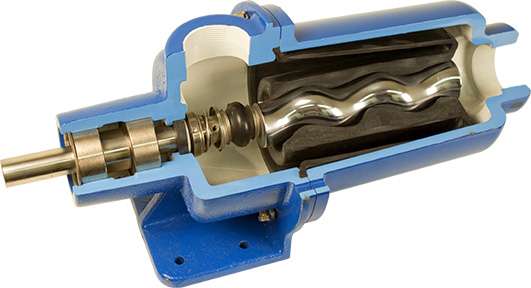
Key Components of Progressive Cavity Pumps
1. Rotor
The rotor is a helical screw that rotates within the stator. It creates cavities that trap fluid and transport it through the pump. The rotor’s design is crucial for efficiency and flow rate. Generally made from durable materials, it is essential that the rotor withstands wear and tear, especially when handling abrasive or corrosive substances.
2. Stator
The stator is a rubber or elastomeric tube with a helical cavity molded inside. It encases the rotor and works in conjunction with it to move the fluid. The stator’s flexibility allows it to maintain contact with the rotor, creating a seal that prevents leakage. Its material selection is critical, as it must resist degradation from the fluids it handles.

3. Drive Shaft
The drive shaft connects the rotor to the motor. It transmits the rotational motion necessary to turn the rotor. A well-designed drive shaft is vital for the pump’s performance, as it affects the efficiency and reliability of the pump. Proper alignment and support are also essential to prevent undue stress and wear.
4. Bearings
Bearings support the rotor and shaft, allowing for smooth rotation. They reduce friction and wear between moving parts, contributing to the pump’s longevity. Quality bearings are crucial, especially in high-load applications, to ensure efficient operation and minimize downtime.
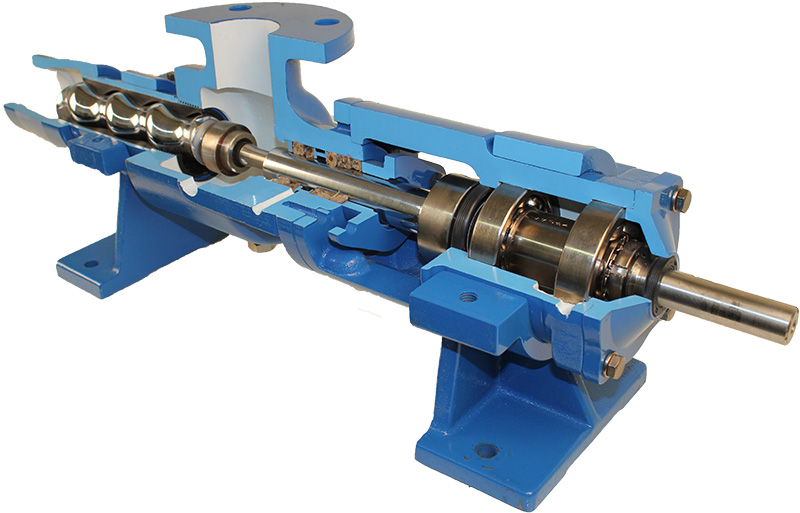
5. Discharge Head
The discharge head is where the fluid exits the pump. It may include various fittings and connections that facilitate the efficient transfer of fluids to the desired destination. The design of the discharge head affects flow dynamics and should be tailored to the specific application.
6. Inlet Suction
The inlet suction is where the fluid enters the pump. Proper inlet design ensures that the pump operates efficiently and prevents cavitation, which can lead to damage over time. It is important to consider the layout of the piping and any potential obstructions that may affect fluid flow.
7. Flow Control Valves
Flow control valves regulate the amount of fluid entering the pump. They are essential for maintaining optimal operating conditions and ensuring that the pump performs at its best. These valves help prevent issues such as overpressure or cavitation, which can lead to pump failure.
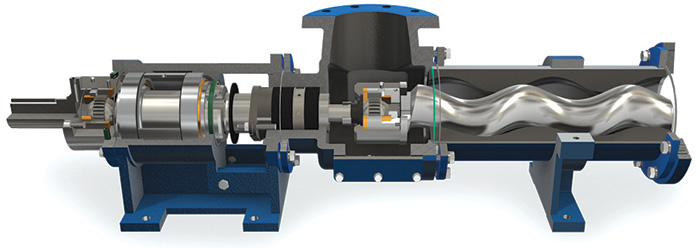
8. Wear Plates
Wear plates protect the pump’s internal components from abrasion caused by the fluid being pumped. They are usually made from hard materials that can withstand harsh operating conditions. Regular inspection and replacement of wear plates are essential to maintain pump efficiency and prolong its lifespan.
Importance of Each Component
Each part of a progressive cavity pump plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency and reliability of the pump. Understanding how these components work together can help operators troubleshoot issues and optimize performance. Regular maintenance and timely replacement of worn parts can prevent costly downtime and extend the life of the pump.
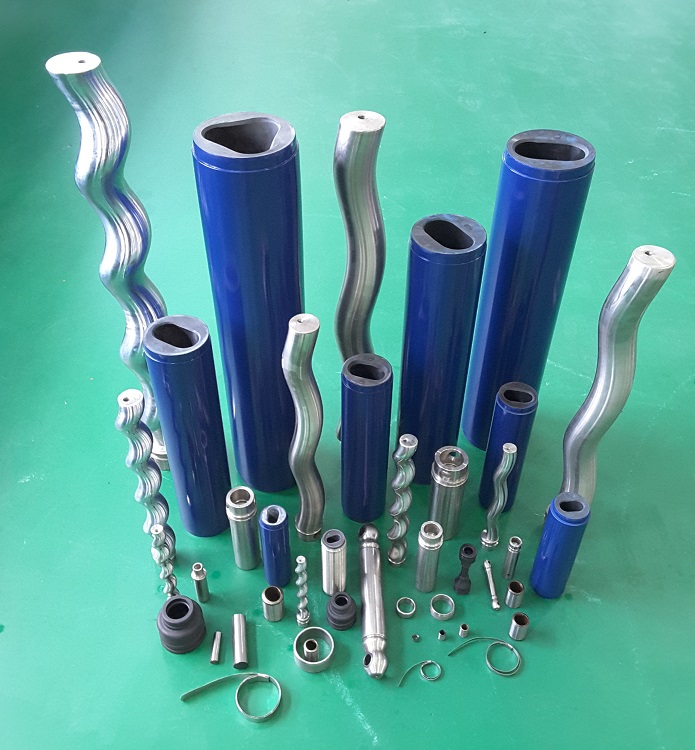

Maintenance Tips for Pump Parts
Regular Inspection
Routine inspections of the pump parts are vital. Checking for signs of wear, leaks, or misalignment can help identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems.
Lubrication
Proper lubrication of moving parts, like the bearings and drive shaft, is essential for smooth operation. Ensure that all lubricants used are compatible with the pump’s materials and the fluids being handled.
Cleaning
Keeping the pump clean from debris and build-up is crucial. This ensures that all components function correctly and minimizes the risk of blockages or damage.
Replacement of Worn Parts
Be proactive about replacing worn or damaged components. Using OEM parts ensures compatibility and maintains the integrity of the pump.
Conclusion
Understanding the parts of a progressive cavity pump is essential for effective operation and maintenance. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring efficient fluid transfer, and regular care can prevent failures and prolong the life of the pump. With proper knowledge and maintenance practices, operators can ensure their pumps perform optimally, contributing to the overall efficiency of their processes. By investing time in understanding these components, you can avoid costly repairs and downtime, ensuring smooth operations in your industrial applications.