The Moyno Pump Curve is an essential tool for understanding the performance characteristics of Moyno progressive cavity pumps. This guide will cover everything you need to know about the pump curve, its components, how to interpret it, and its importance in various applications.
What is a Moyno Pump Curve?
A Moyno Pump Curve is a graphical representation that illustrates how a Moyno pump performs at different flow rates and heads (pressure). It provides valuable information for selecting, operating, and troubleshooting pumps in various industrial applications.
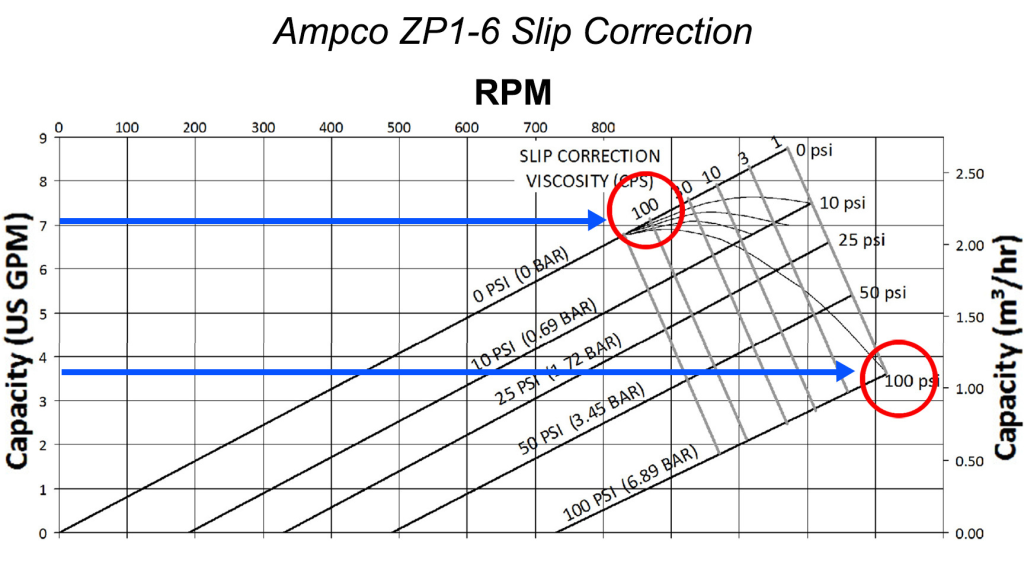
Key Components of the Pump Curve
- Flow Rate (Q):
- Measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM).
- Displayed on the X-axis of the curve.
- Head (H):
- Measured in feet or meters.
- Represented on the Y-axis, indicating the pressure the pump can generate.
- Efficiency Curve:
- Shows the efficiency of the pump at various flow rates.
- Typically represented as a separate line on the graph, indicating the percentage of efficiency.
- Net Positive Suction Head Required (NPSHr):
- Indicates the minimum pressure required at the pump inlet to prevent cavitation.
- Often represented as a horizontal line on the curve.

How to Read the Moyno Pump Curve
- Understand the Axes:
- The X-axis represents the flow rate.
- The Y-axis represents the head (pressure).
- Determine the Operating Point:
- Locate your desired flow rate on the X-axis.
- Draw a vertical line up to the pump curve to find the corresponding head.
- Assess Efficiency:
- Identify the efficiency curve on the graph.
- Determine the efficiency at your operating point to ensure optimal performance.
- Verify NPSHr:
- Check that the available Net Positive Suction Head (NPSH) exceeds the required NPSHr to avoid cavitation issues.
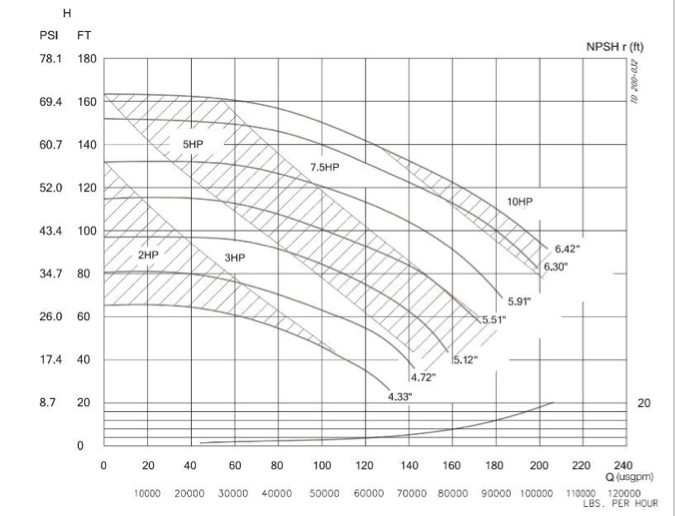
Applications of the Moyno Pump Curve
- Pump Selection:
- Helps in selecting the right pump size and type based on the specific application needs.
- Performance Analysis:
- Enables operators to predict how a pump will perform under varying conditions, which is crucial for system design.
- System Optimization:
- Assists in optimizing the entire pumping system by ensuring the pump operates efficiently within its designated range.
- Troubleshooting and Maintenance:
- Comparing actual pump performance to the pump curve can help identify issues and guide maintenance efforts.